Fasting Zones
Understand what's happening in your body at each stage of your fast.
This content is educational and based on our interpretation of published research. See our Terms of Service for important disclaimers.
During the fed state, your body is actively digesting food and absorbing nutrients. Blood sugar rises as carbohydrates are broken down, triggering insulin release to help cells absorb glucose for energy.
Benefits
- Nutrient absorption
- Energy from food
- Muscle protein synthesis
How Fasting Zones Work
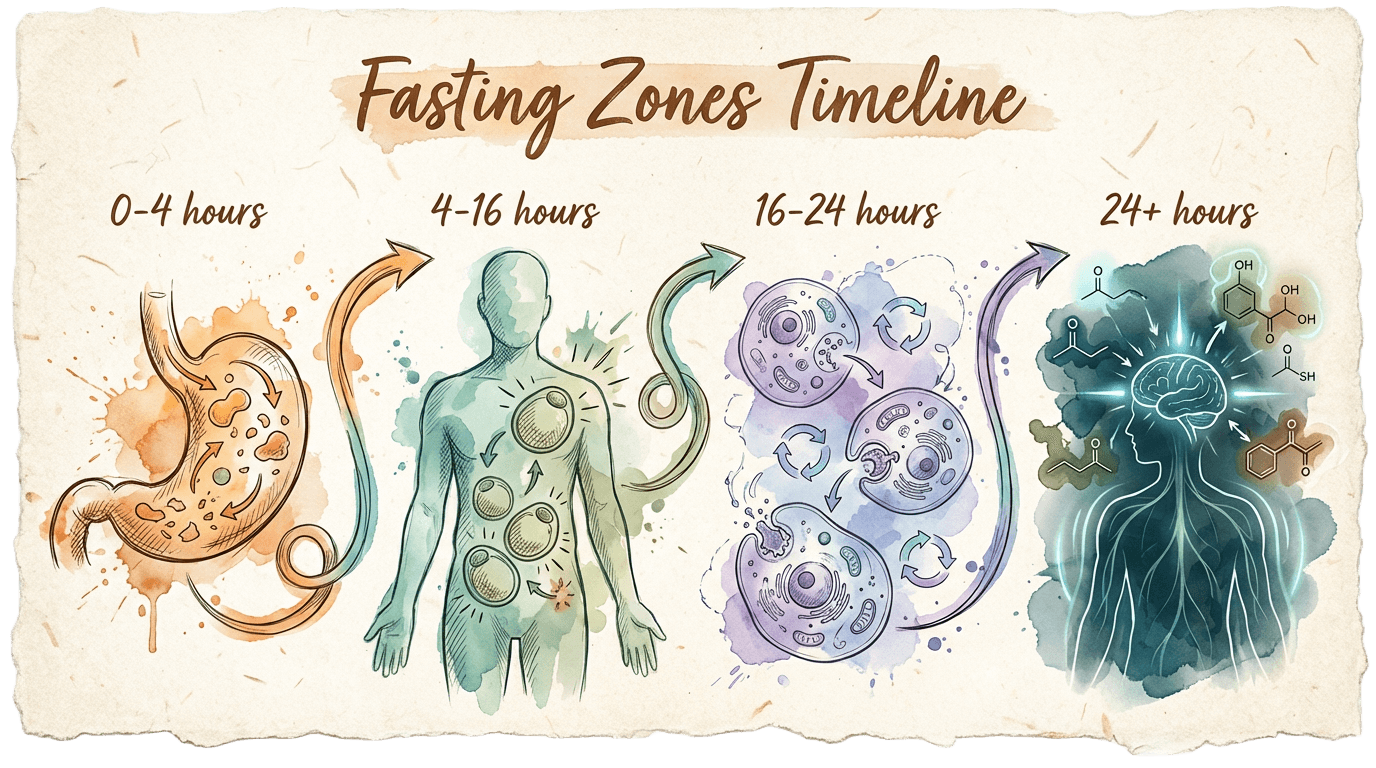
When you fast, your body goes through distinct metabolic phases. Research shows the "metabolic switch" from glucose to fat burning typically occurs between 12-36 hours, depending on the individual. Understanding these zones can help you set meaningful fasting goals.
The Five Phases
Your body digests food and uses glucose for energy.
Liver glycogen depletes and your body transitions to burning fat.
Your body burns fat as primary fuel. Growth hormone increases significantly.
Cellular cleanup increases. Requires medical supervision.
Potential stem cell and immune effects. Requires medical supervision.
Individual Variation
These time ranges are approximate and vary significantly between individuals. Your transition times depend on metabolism, activity level, what you ate before fasting, and your body's adaptation. Those on low-carb diets or who exercise may enter ketosis faster. Some research shows ketosis onset anywhere from 12 to 28 hours. The NHS Diabetes guidance notes that intermittent fasting can help with weight loss and improving insulin resistance.
Fasting is not appropriate for everyone. Do not fast if you:
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding
- Are under 18 years old
- Have a history of eating disorders
- Have type 1 diabetes or use insulin
- Take medications that require food
- Have kidney or liver disease
- Have gout or a history of gallstones
- Are underweight or malnourished
- Are 65+ with chronic health conditions
- Are recovering from surgery
If you take blood thinners, blood pressure, or diabetes medications, consult your doctor before fasting. Diabetes UK advises that if you take insulin or tablets that can cause hypos, speak to your healthcare team before changing your eating pattern. Extended fasts (24+ hours) require medical supervision.
Track your fasting zones in real-time
Private • No account • Works offline
See exactly which zone you're in as you fast. The timer updates in real-time and shows your progress towards each milestone. Tap any zone to learn more about what's happening in your body.
Tip: 16:8 is a great starting point for most people.